Are male and female brains different? This question has been the subject of much debate and controversy. While popular belief suggests that men and women have inherently different brain structures and functions, recent scientific research has shed new light on this topic. Advancements in neuroscience have provided us with a deeper understanding of the human brain, challenging long-held assumptions about gender differences. Studies have shown that while there may be some slight variations in brain structure between males and females, the overall differences are not as significant as previously believed.
It’s important to note that gender differences in the brain should not be misconstrued as determinants of behavior or abilities. The complexity of our brains and the interplay of various factors, such as genetics, environment, and individual experiences, make it difficult to draw definitive conclusions about gender-based brain dissimilarities. In this article, we will explore the current scientific consensus on udintogel male and female brain differences, examining the research and dispelling common misconceptions. So, let’s dive in and uncover the truth about whether male and female brains are truly different.

Understanding the Structure and Function of the Male Brain
The human brain, regardless of gender, is a complex and intricate organ. However, when looking at the male brain specifically, certain structural characteristics can be identified. Men are generally found to have larger brains than women in terms of volume. The larger size of the male brain is primarily due to the larger physical stature of men compared to women as brain size generally correlates with body size. However, a bigger brain does not necessarily correlate with superior cognitive abilities or intelligence.
In addition, the male brain is also observed to have more connections within each hemisphere, particularly in the back of the brain. These connections are thought to enhance perception and action skills. Furthermore, the male brain has more gray matter, which is responsible for processing information and executing actions. The concentration of gray matter in certain areas of the male brain is linked to more focused, albeit less multitasking, cognitive processing.
Functionally, men are often thought to have a predisposition towards spatial tasks such as navigation and object rotation. Studies have attributed this to a higher concentration of neurons in the parietal lobes, which are responsible for space perception and action. However, it is crucial to remember that individual differences and environmental factors can greatly influence these general tendencies.
Understanding the Structure and Function of the Female Brain
The female brain, while smaller in volume compared to the male brain, exhibits its own unique characteristics. For instance, women are found to have more connections between the two hemispheres of the brain. This inter-hemispheric communication is facilitated by a thicker corpus callosum, the bridge between the two brain halves. This structure allows women to use both sides of their brain more simultaneously, which is often associated with better multitasking abilities.
Moreover, the female brain has a higher proportion of white matter compared to the male brain. White matter is responsible for communication between different areas of the brain, which supports the coordination of various tasks. The female brain is also denser in certain areas, including the frontal lobe responsible for problem-solving and decision-making, and the limbic cortex responsible for controlling emotions.
In terms of function, women are often reported to excel in verbal tasks and memory recall. The left hemisphere, which is typically dominant in language processing, is more active in women during language tasks. Additionally, women are generally better at remembering words and faces, which is linked to increased activity in the brain’s hippocampus, a region critical for memory. However, as with the male brain, individual variations and environmental influences can significantly alter these patterns.
Hormonal Differences and Their Impact on Brain Development
Hormones play a significant role in the development and function of the brain. The primary sex hormones, estrogen in women and testosterone in men, have profound effects on brain structure and function. These hormones are not only responsible for the physical differences between men and women but also influence brain development and function throughout life.
For example, testosterone has been found to influence the development of areas in the male brain associated with spatial abilities. Conversely, estrogen has been linked to enhancing verbal ability in the female brain. These hormones also influence mood and emotions, with estrogen thought to enhance mood and emotional expressiveness in women, while testosterone promotes competitiveness and aggression in men.
However, it’s essential to understand that hormonal influences are not deterministic. The brain is a highly adaptable organ, capable of significant plasticity. This means that while hormones can influence brain development and function, they do not dictate behavior or abilities. Individual experiences, environment, and genetics also play a critical role in shaping our brains.
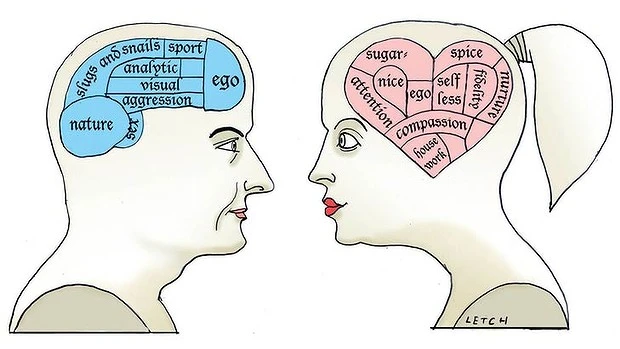
Cognitive Differences Between Males and Females
Cognitive differences between males and females, while often overstated, do exist to some extent. As previously mentioned, men generally perform better in spatial tasks, such as navigating a route or rotating objects mentally. This is thought to be due to the higher concentration of neurons in the parietal lobes of the male brain.
On the other hand, women typically outperform men in verbal tasks and memory recall. Women are better at remembering words, faces, and multi-itemed events. They also tend to use more words when communicating and can process multiple pieces of information at the same time more efficiently. These abilities are attributed to the increased activity in the language-dominant left hemisphere and the larger hippocampus in the female brain.
However, it’s important to stress that these differences are averages and there is considerable overlap between men and women. Many men excel in verbal tasks, just as many women excel in spatial tasks. Furthermore, the observed differences are relatively small and the individual’s abilities can be greatly influenced by environmental factors, education, and individual experiences.
Emotional and Social Differences Between Males and Females
Emotional and social differences between males and females are often more linked to societal and cultural expectations than to neurological differences. However, some research suggests that women are generally more empathetic and better at reading emotional cues than men. This could be related to the larger limbic system in women, which regulates emotions.
Men, on the other hand, are often seen as more aggressive and competitive, traits that are typically linked to the influence of testosterone on the male brain. However, it’s worth noting that aggression and competitiveness are heavily influenced by cultural factors and individual experiences, and are not solely determined by biology.
Socially, women are often thought to be more skilled at multitasking and coordinating social interactions, which could be due to the greater connectivity between brain hemispheres. However, again, these are general tendencies and there are many individual variations.
Debunking Common Myths About Male and Female Brain Differences
There are many misconceptions and myths about male and female brain differences. One prevalent myth is that men are more logical and women are more emotional. While it’s true that men and women might process emotions differently, it’s not accurate to say that one gender is more emotional or logical than the other. Both sexes are capable of logical thinking and emotional processing.
Another common myth is that women are naturally better at multitasking. While some studies suggest that women might be better at handling multiple tasks at once, this difference is not significant and there’s a great deal of overlap between individuals. Both men and women can be good or bad at multitasking depending on various factors like personality traits, work habits, and more.
It’s also worth debunking the myth that a larger male brain means greater intelligence. Brain size does not equate to intelligence, and intelligence is a multi-faceted trait that is influenced by a myriad of factors including genetic, environmental, and personal experiences.

The Influence of Societal and Cultural Factors on Brain Development
The social and cultural environment in which a person grows up can significantly influence brain development and function. Societal and cultural expectations often dictate the roles and behaviors of men and women, which can, in turn, shape their brains.
For example, girls are often encouraged to be nurturing and communicative, which could enhance the development of language and empathetic skills. Similarly, boys are often encouraged to be competitive and independent, which might foster spatial and motor skills. These socially conditioned behaviors can then be misinterpreted as innate gender differences.
Moreover, societal biases and stereotypes can also influence how we perceive and interpret gender differences. For instance, the stereotype that men are better at math can lead to more men pursuing careers in fields like engineering and physics. This doesn’t necessarily mean that men are inherently better at math, but rather that societal expectations and biases can shape our interests and abilities.
The Implications of Male and Female Brain Differences in Education and Career Choices
Understanding the subtle differences between male and female brains can have important implications in education and career choices. For example, recognizing that boys might have a natural inclination towards spatial tasks could lead to the development of teaching methods that leverage this strength. Similarly, understanding that girls might excel in verbal tasks can be used to foster their skills in this area.
When it comes to career choices, it’s important not to let stereotypes or misconceptions guide decisions. While certain fields might be dominated by one gender, this doesn’t mean that the other gender is incapable of succeeding in those fields. Employers and educators should strive to create environments that are inclusive and supportive of all individuals, regardless of their gender.
Furthermore, understanding that our brains are capable of significant plasticity can help combat gender stereotypes. With the right training and experiences, individuals can develop a wide range of skills and abilities, regardless of their gender.
Embracing Diversity and Understanding Individual Differences
In conclusion, while there are some differences between male and female brains, these differences are small and there’s a great deal of overlap between the sexes. It’s also important to remember that our brains are highly adaptable and can be shaped by our experiences and environment.
Rather than focusing on gender differences, we should embrace diversity and strive to understand individual differences. This approach can help us create more inclusive societies and institutions, where everyone has the opportunity to reach their full potential, regardless of their gender.
In the end, the human brain, whether male or female, is a remarkable organ, capable of extraordinary feats. By appreciating the complexity and diversity of our brains, we can better understand ourselves and those around us. If you found this exploration enlightening and are curious to delve deeper into the personalities that shape our global landscape, we invite you to read our fascinating article about Xi Jinping. It’s an insightful look into the life and policies of one of the world’s most influential leaders, offering a unique perspective on how individual leadership styles can impact global politics and society.